about
about

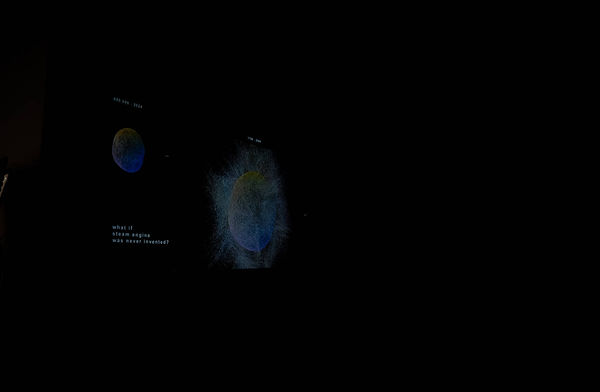
What if Steam Engine was Never Invented?
speculative design / data-visualization / climate art
data visualization project
exhibited in MIT ACT Cube
The Anthropocene is a proposed geological epoch that follows the Holocene, defined by the lasting impact of human activity on Earth’s systems. Climate change, biodiversity loss, and the global spread of synthetic materials—from plastics to nuclear fallout—are not isolated events, but interconnected signals of this shift.
The scale of the Anthropocene is difficult to grasp. Climate data operates at planetary scales, while human experience is local and immediate. This gap is where climate communication often breaks down.
This project uses the butterfly effect as a narrative bridge—linking small, perceivable changes to large-scale atmospheric consequences—so complex climate data can be understood at a human scale.

Using speculative design, the project imagines an alternative climate history through two animated visualizations of atmospheric CO₂. In both, particles move faster as concentration increases, translating numerical data into perceptible motion.
-
The first animation traces CO₂ levels from prehistory to the present, revealing how abruptly human influence alters a previously slow-moving system.
-
The second compares two futures from 1700 to 2500: one following current emissions trajectories, and another imagining a world in which the Industrial Revolution never occurred.
By placing historical data and scientific research alongside a counterfactual scenario, the work makes the scale of human impact visible. Rather than predicting outcomes, it asks a quieter but more unsettling question: how different could the planet have been—and how different might it still become?
The CO2 concentration data for the project was derived from various sources, including historical data, projected data, and speculative data on potential scenarios had the Industrial Revolution not occurred. This divergence began in the year 1700, a point when CO2 concentration significantly altered our lives.
The data includes:
-
Baseline (with Industrial Revolution):
-
-800,000 - 1750 - historic
-
1750 - 2024 - real-dataset
-
2024 - 2100 - prediction
-
-
What-if (without industrial revolution)
-
-800,000 - 1750 - historic
-
1750 - 2100 x 2500 - (my) prediction
-

Throughout the Earth's history, carbon dioxide levels have generally changed very slowly, fluctuating within a certain range to give organisms their ecosystems sufficient time to adapt to climate change through both evolution and migration. However, industrial activity has greatly disrupted that balance.